What is revenue cycle management in healthcare?

Collecting more of the billions left on the table means understanding revenue cycle management
This post was published July 12, 2018, and updated June 19, 2019, and September 15, 2022.
“A billion here, a billion there, and pretty soon you’re talking real money.” That was the famous quote attributed to US Senator Everett Dirksen — although he probably never said it.1 Today, it’s become the theme of revenue cycle management in medical billing.
What is revenue cycle management?
A common definition of revenue cycle management in healthcare is “all the administrative and clinical functions that contribute to the capture, management and collection of patient service revenue.”
The RCM process begins as soon as patients make appointments for your services and continues until you receive full payment from both insurers and patients. A true RCM solution unifies the key components of practice management, electronic health records and claims processing. It creates an efficient workflow that helps you collect revenue while enhancing the patient experience.
What are the major revenue cycle management challenges?
In the United States, revenue cycle management in medical billing requires considerable expertise, attention and perseverance to navigate. Many practices fail to recognize the importance of revenue cycle management in healthcare, relying instead on disparate systems and disjointed processes that can sometimes result in payments getting delayed or denied.
Revenue can seep out from countless cracks in the system, including inadequate monitoring of underpayments and denials, fumbles in patient collections, errors in insurance credentialing and policy coverage, services not even billed, clunky hardware and software, and insufficient staffing and training in the billing area.
Why is revenue cycle management important in healthcare?
A significant loss of cash flow can have a serious impact on the overall success of a practice, and even before the COVID-19 pandemic, billing errors and rejected claims were costing providers billions of dollars per year. Going forward, effective healthcare revenue cycle management could become even more critical.
In 2022, the credit agencies announced sweeping changes in how they would report medical debt, omitting most existing debt and delaying reports of new collection activity. The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau estimated that 43 million credit reports showed roughly $88 billion in medical bills.2 The changes are designed to help consumers retain access to credit, but they may also reduce creditors’ leverage to collect medical debt.
In 2021, the White House issued a new rule under the No Surprises Act to limit patients’ out-of-pocket costs. It provided that health insurers and medical providers settle their differences through a new arbitration system when they couldn’t agree on charges.3
Grasp the revenue cycle management process in medical billing
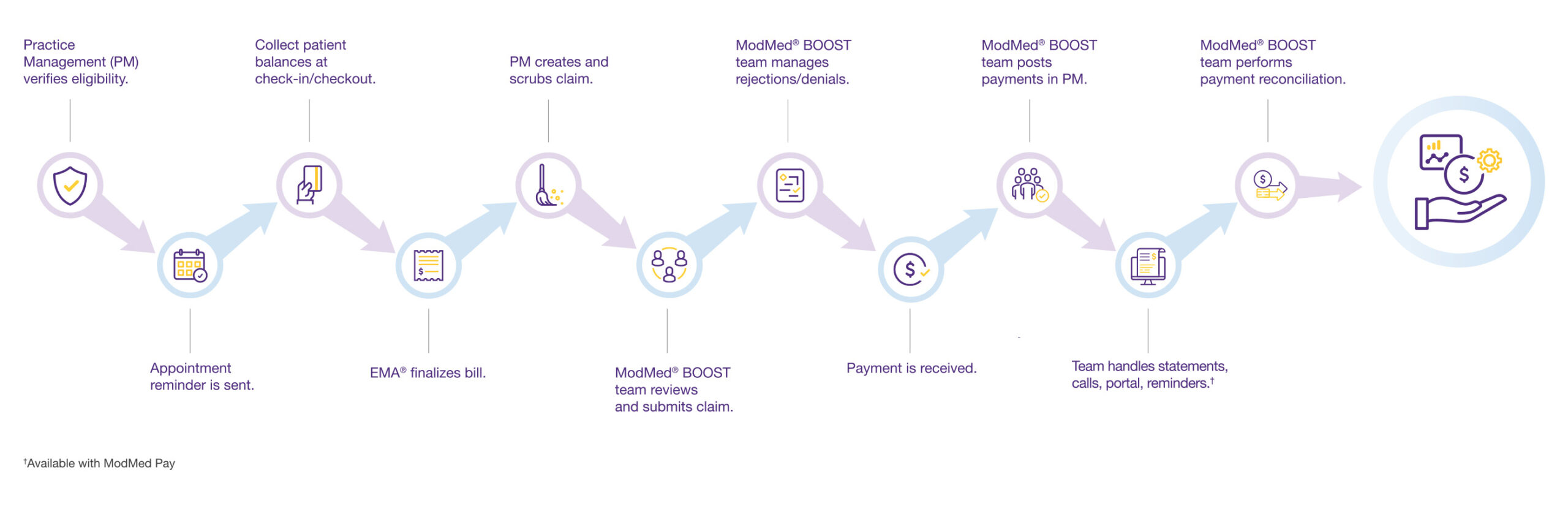
Understanding revenue cycle management, which involves so much more than just billing, means understanding all the people, processes and technologies required to increase reimbursements by insurers and payments by patients. Here are the major steps of an RCM service.
1. Eligibility Verification. Before patient appointments, the practice management system automatically checks eligibility to avoid problems with reimbursement.
2. Patient Check-In. Upon arrival, patients check themselves in through a patient portal, their own smartphones or a kiosk in your lobby.
3. Collection. Patient balances are collected at check-in (and checkout).
4. Billing. During documentation, an integrated electronic health records system creates a bill and suggests codes and modifiers for services.
5. Claim Creation. The practice management system creates and scrubs claims for accuracy.
6. Claim Submission. Before sending out claims, the billing team reviews them for accuracy, then releases them to the clearinghouse.
7. Claim Rejection. If the clearinghouse rejects a claim, it is returned to the RCM team for correction and resubmission for payment.
8. Payment Receipt. Insurance payments are transferred to your bank account and posted to patient accounts in the practice management system.
9. Patient Payments. To help collect patient balances, the system provides detailed statements, inbound call handling and a payment portal.
10. Posting. The billing team makes sure that all payments are posted in the practice management system.
11. Account Reconciliation. The RCM team reviews accounts to confirm that everything adds up, comparing the claims sent with the payments received.
How are practices tying together the revenue cycle?
Our ModMed® BOOST team offers all the above-listed steps of revenue cycle management in healthcare. Working with our integrated Practice Management and EMA® EHR system, we can help your office put the right processes in place to gain vital transparency and run more smoothly, so you can focus on what matters most — patient care. Reach out for a complimentary cash flow analysis to identify opportunities.
Discover how ModMed BOOST can support your bottom line.
References
1. “A Billion Here, a Billion There,” The Dirksen Congressional Center website (2021)
2. AnnaMaria Andriotis, “Most Medical Debts to Be Removed From Consumers’ Credit Reports,” The Wall Street Journal (2022 March 18)
3. Stephanie Armour, “Medical Cost Disputes to Be Settled by Arbitrator,” The Wall Street Journal (2021 Sept. 30)
This blog is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal or medical advice. Please consult with your legal counsel and other qualified advisors to ensure compliance with applicable laws, regulations and standards.



